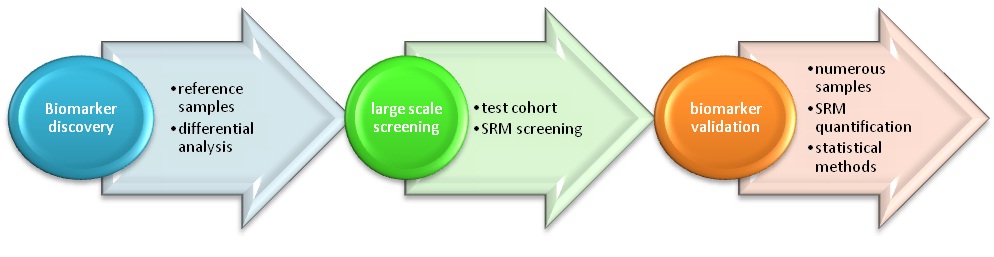
The discovery of potential targets (or biomarkers) associated with the investigated biological event is a key point in the treatment or the diagnostic test conception.
The difference between good health and disease is often visible at the proteome level. This difference may be followed for perfecting a diagnostic test or designing a drug treatment.
Our approaches are mainly based on high performance nano-chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and allow identifying and quantifying simultaneously hundreds of proteins.
Biological specimens can be body fluids like plasmas, sera, urines,tears or tissues or cell cultures.
It is recommended to analyse at least 6 samples on each tested condition in order to be statistically relevant.
This method allows comparison of samples (treated vs untreated) using their mono- or bi-dimensional LC-MS profiles and thus the identification of discriminating components by MS/MS .It allows also the relative quantification and gives the advantage of accessing to powerful statistics analysis. Furthermore, there is neither sample labelling step nor complex and costly sample derivation.
This “label free” approach has the advantage of being cheap and easy to handle. However, depending on the demand, we can realize isobaric labelling (TMT®) which remains more expensive.
The protein comparison to existing databases allows the differentiating protein identification. If these are unknown, it is possible to characterize them.
The relevant number of clinically documented cohort samples is several tens.
Absolute quantification of components by targeted method (PRM)
This method is based on the follow-up of one protein and its corresponding peptides MS/MS fragmentation data which lead to its absolute quantification.
The PRM type targeted methods are considered as the most selective and sensitive mass spectrometry methods since using the PRM scan mode, only peptides of interest are analyzed and thus improves the sensitivity and signal to noise ratio. The use of a high resolution instrument (Orbitrap) coupled to a quadrupole performing accurate ionic filtration of parent ions allows obtaining screening and quantification methods for which the sensitivity/specificity compromise is better than on a triple quadrupole instrument in classical PRM mode. The advantage of this targeted method type is to be able to follow the proteins of interest in a robust and fast way. Furthermore, this method is easily transposable on triple quadrupole instrument type.
Extended clinical study compared to a reference technique.